C Double Bond O Hybridization

A triple bond is formed with an sp hybridized orbital and two p orbitals from each atom.
C double bond o hybridization. One way to think about that is the increased s character. It is experimentally observed that bond angles in organic compounds are close to 109 o 120 o or 180 o according to valence shell electron pair repulsion theory electron pairs repel each other and the bonds and lone pairs around a central atom are generally separated by. The simple view of the bonding in carbon oxygen double bonds. The c o double bond absorbs infrared light at wavenumbers between approximately 1600 1900 cm 1 5263 nm to 6250 nm.
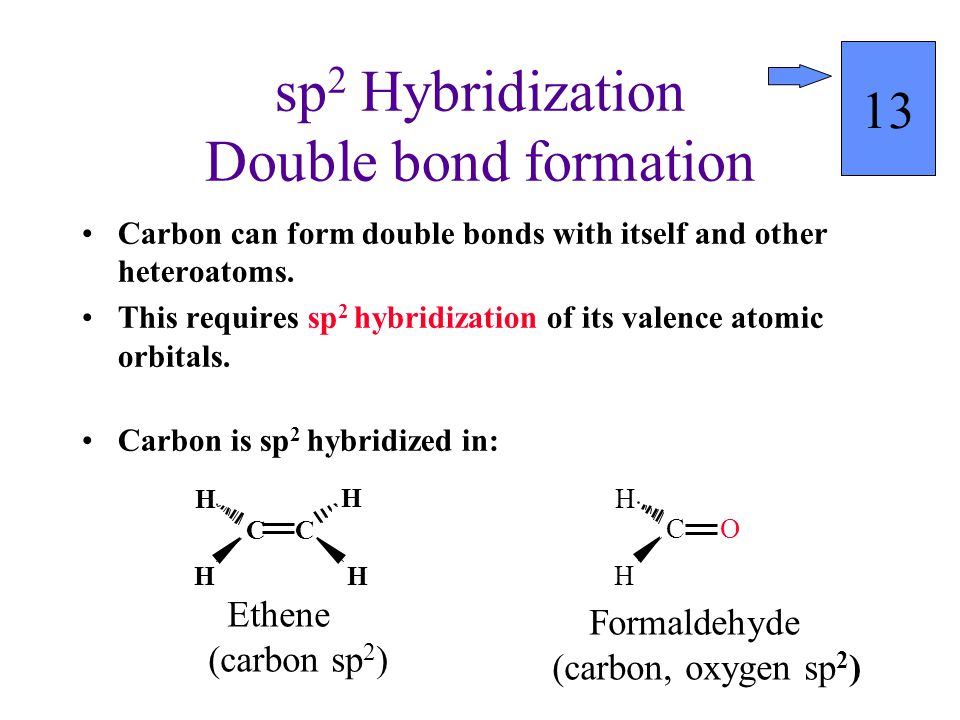
Sp2 hybridizationin ethene carbon sp 2 hybridizes because one π pi bond is required for the double bond between the carbons and only three σ bonds form per carbon atom. This increased s character means electron density is closer to the nucleus and that s going to make this lobe a little bit shorter than before and that s going to decrease the distance between these two carbon atoms here. Ethene c 2 h 4 has a double bond between the carbons. The three hybridized orbitals explain the three sigma bonds that each carbon forms.
Ethene has a double bond between the carbons. Carbon atoms can also form double bonds in compounds called alkenes or triple bonds in compounds called alkynes. Where the carbon oxygen double bond c o occurs in organic compounds it is called a carbonyl group. We are going to look at the bonding in methanal but it would equally apply to any other compound containing c o.
A double bond is formed with an sp 2 hybridized orbital and a p orbital that is not involved in the hybridization. Similarly for a triple bond formation like for that of acetylene molecule there is sp hybridization between 1 s and 1 p orbital of the carbon atom. Image to be added soon here there are 2 c h bonds and a triple c c bond. And the reason for this is the fact that the steric number of the carbon is two there are only two atoms of oxygen connected to it and in order to keep two atoms at 180 o which is the optimal geometry the carbon needs to use two identical.
Hybridization was introduced to explain molecular structure when the valence bond theory failed to correctly predict them. The exact location of the absorption is well understood with respect to the geometry of the molecule. In this case carbon will sp 2 hybridize. Thus the sp 2 hybridization theory explains the double bond the trigonal planar structure in ethylene molecule.
Nucleophilic abstraction is used to produce carbon dioxide. For example in the carbon dioxide co 2 the carbon has two double bonds but it is sp hybridized. The simplest compound containing this group is methanal.